Hydraulic power unit of full electric stacker
Cat:DC series hydraulic power unit
This hydraulic power unit of full electric stacker is specially designed for full electric stacker. It is integrated by a high-pressure gear pump, a D...
See DetailsIn manufacturing, HPU stands for Hydraulic Power Unit.
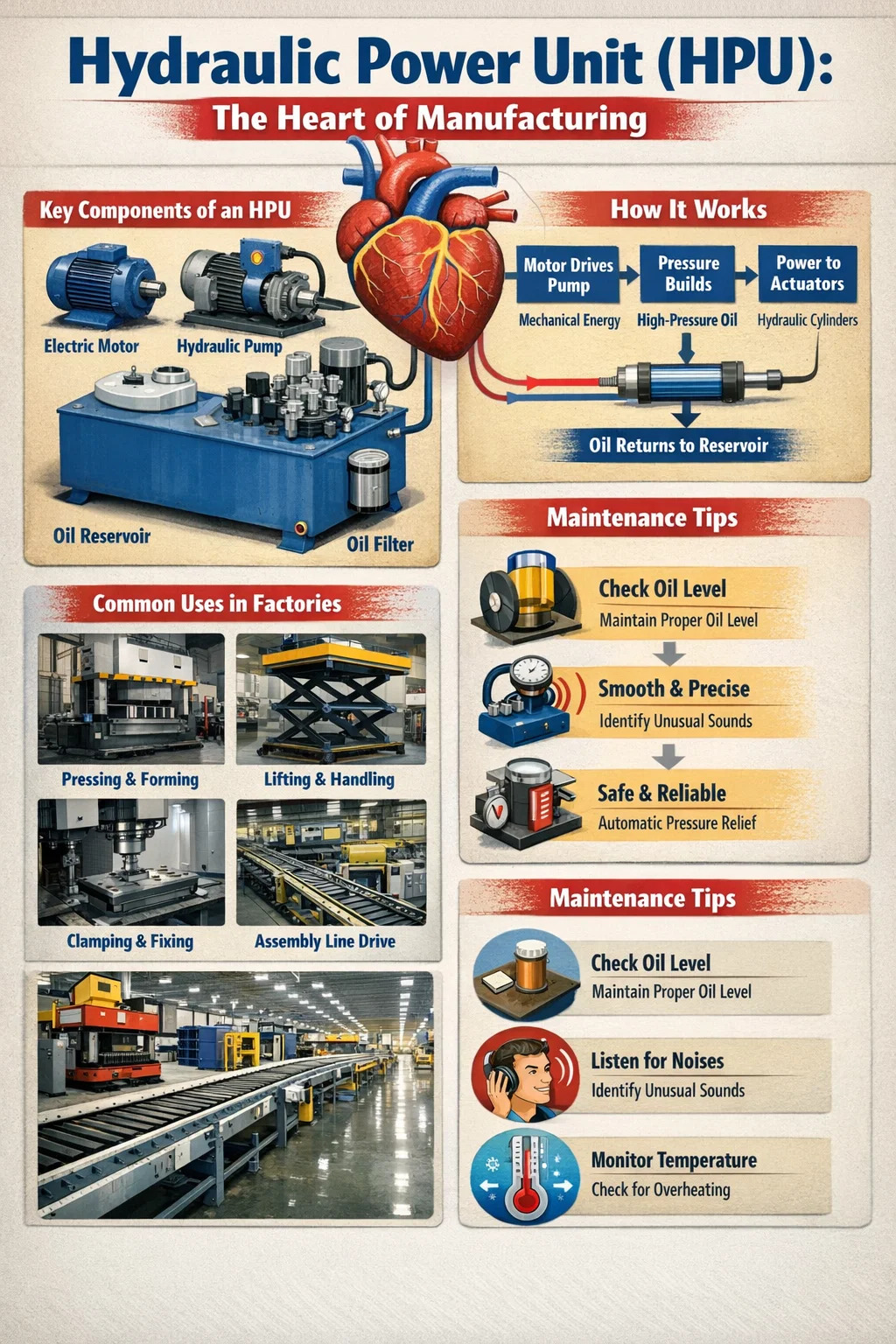
Simply put, if you compare the machinery in a factory to the human body, the hydraulic power unit is equivalent to the "heart." It generates power by compressing a fluid (usually hydraulic oil) and then delivers this power to the parts that need to do the work, such as robotic arms, presses, or lifting platforms.
Content
A complete hydraulic power unit (HPU) is like a small power station, mainly consisting of the following parts:
Motor: This is the power source of the system, usually powered by electricity, driving the pump to rotate.
Hydraulic Pump: Located next to the motor, it is responsible for drawing fluid from the oil tank and pressurizing it.
Reservoir: Used to store hydraulic oil, it also serves to cool the oil and settle impurities.
Control Valves: Equivalent to "taps" or "switches," they determine where the oil flows and how much pressure is applied.
Filter: Ensures the cleanliness of the oil, preventing dirt from damaging precision parts.
Its working principle is actually quite simple:
Energy Conversion: The motor rotates, driving the hydraulic pump to convert mechanical energy into fluid pressure energy.
Power Transmission: High-pressure oil flows through pipes to the machine's actuators (such as hydraulic cylinders).
Action Completion: The high-pressure oil pushes the piston inside the cylinder, generating enormous thrust or pull, allowing heavy machinery to move.
Continuous Cycle: After completing its work, the oil flows back to the reservoir, is filtered, and prepared for the next cycle.
In manufacturing workshops, any task involving "heavy lifting" or "precise movement" basically relies on a hydraulic power unit.
Pressing and Forming: For example, stamping presses used to manufacture car parts require hundreds of tons of pressure to press steel plates into shape.
Lifting and Handling: Factory lifting platforms and automatic loading platforms are all powered by it.
Clamping and Fixing: When machining parts on CNC machine tools, it is used to firmly clamp the workpiece, ensuring that it does not move during processing. Assembly Line Drive: Drives heavy conveyor belts or large turntables smoothly.
Immense Power: Compared to purely electric motors, hydraulic systems can generate extremely large forces in a very small volume.
Smooth and Precise: The speed of the fluid flow can be finely adjusted, so the machine moves very smoothly without sudden changes in speed.
Safe and Reliable: As long as the safety valve is properly set, if the pressure exceeds the limit, the oil will automatically flow back into the oil tank, preventing damage to the machine.
To keep this "heart" beating for a long time, workers usually:
Check the oil level: Ensure there is enough oil in the tank to prevent the pump from "running dry."
Listen to the sound: A normal hydraulic power unit has a dull, even sound. If there is a harsh screeching sound, it indicates that air may have entered the system or the filter is clogged.
Check the temperature: If the casing is hot to the touch, it indicates a cooling problem and requires shutting down the machine for inspection.